CS/Data Structure
[ 자료구조 ] 연결 리스트 ( Linked List )
KimBangg
2021. 8. 5. 15:28
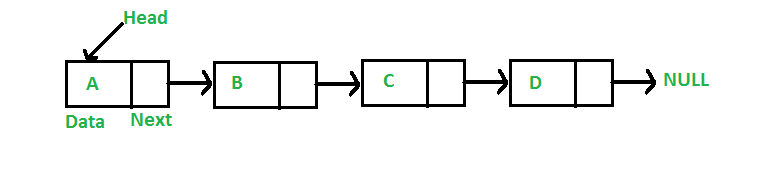
1. 연결 리스트의 특징
- 메모리가 허용하는한 요소를 제한없이 추가 할 수 있습니다.
- 배열과 다르게, 메모리가 연속적으로 저장 되어 있지 않기 때문이다.
- 탐색은 O(n)이 소요됩니다.
- 인덱스가 존재 하지 않기 때문에, 찾는 대상을 만날 때까지 순회를 해야합니다.
- 요소를 추가하거나 제거 할 때는 O(1)이 소요됩니다.
- 단, 요소의 추가와 삭제를 위해서는 장소의 탐색이 발생하기에 이 작업을 최소화 하는 것이 중요합니다.
- 링크드 리스트의 유형으로는 [Single, Double, Circular] 총 3가지가 존재합니다.
2. 배열과의 차이점
1. 배열과 연결 리스트의 가장 큰 차이점은 메모리에서 발생합니다.
2. 연결 리스트는 산발적, 배열은 연속적으로 이루어져있습니다.
( => 배열은 연속적인 메모리 구조를 가지고 있기에, 삽입과 삭제를 하는 경우 선형 시간 (O(n))이 발생합니다. )
3. 단일 연결 리스트
각 노드는 자신의 값과 다음 노드를 가리키는 next 함수를 가지고 있습니다.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
탐색은 헤드에서 시작해서 원하는 값을 찾을 때까지 순회합니다. => O(n)
find(value) {
let curNode = this.head;
while ( curNode.value !== value ) {
curNode = curNode.next
}
return curNode;
}
append 연산은 연결 리스트의 끝에 새로운 값을 추가합니다.
append(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
// 값이 비어 있는 경우,
if ( this.head === null ) { // 새로운 값을 head & tail로 설정합니다.
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
else {
this.tail.next = newNode; // 테일 뒤에 값을 붙이고
this.tail = newNode; // 새로운 값을 끝 값으로 변경합니다.
}
}
특정 위치 뒤에, 값을 추가하는 Method
insert(node, newValue) { // 특정 위치 뒤에, 값을 추가하는 Method
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
}
삭제 하려고 하는 연산과 만날 떄 까지 이동하여, 다다음을 next로 변경해줍니다.
remove(value) {
let prevNode = this.head;
while ( prevNode.next.value !== value ) {
prevNode = prevNode.next;
}
if ( prevNode.next !== null ) {
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
}
전체 코드 ( 사이즈 반환 및 에러 Catch )
// 전체 코드
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class SingleLinkedList {
// Linked List 에서는 head & taill 에 대한 정보 만을 저장한다.
constructor() {
this.length = 0;
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
// N만큼의 시간이 소요된다.
find(value) {
let curNode = this.head;
// 특정 값을 찾을 때 까지 while-loop
while (curNode.value !== value) {
curNode = curNode.next;
if (curNode === null) {
return console.log("Can't find this value in Linked List");
}
}
return curNode;
}
append(newValue) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length += 1;
}
// 탐색을 방지 하기 위해서, 삽입 하고자 하는 위치를 Parameter로 전달
insert(node, newValue) {
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
this.length += 1;
}
//
remove(value) {
let prevNode = this.head;
while (prevNode.next.value !== value) {
prevNode = prevNode.next;
}
if (prevNode.next !== null) {
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
this.length -= 1;
}
display() {
let curNode = this.head;
let displayString = "[";
while (curNode !== null) {
displayString += `${curNode.value}, `;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
displayString = displayString.substr(0, displayString.length - 2);
displayString += "]";
console.log(displayString);
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
}
const linkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
linkedList.append(1);
linkedList.append(2);
linkedList.append(3);
linkedList.append(4);
linkedList.append(5);
linkedList.display();
linkedList.find(3);
linkedList.remove(3);
linkedList.insert(linkedList.find(2), 10);
linkedList.display();
console.log(linkedList.size());